- Where Do Androgen Receptors Exist?
- How do they affect muscle growth?
- The concept of muscle saturation
- Can receptors become full?
- Factors that affect receptor sensitivity
- Is it possible to increase androgen receptors?
- Misconceptions about saturation
- The Function of Natural Hormone Levels
- Practical Tips for Lifters:
- Why do some lifters stop growing?
Muscle growth entails more than simply lifting heavy weights and eating more. There are special switches inside the body known as androgen receptors. These switches respond to hormones such as testosterone. When they turn on, the body begins to build muscle. However, these switches do not function without limitations. Even when more hormones are present, they may eventually cease to produce the same results. This stage is known as muscle saturation. To understand why some people grow faster than others, we must first understand androgen receptors and muscle saturation.
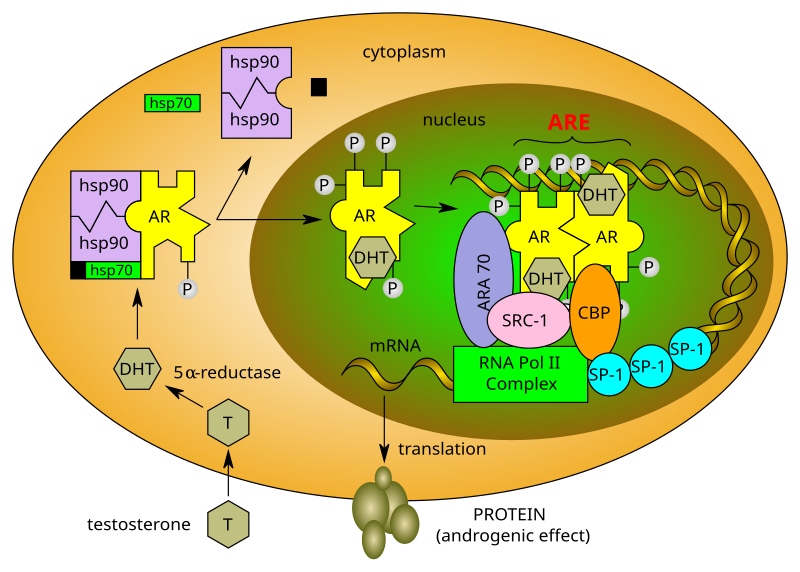
Androgen receptors are small “locks” in the body that respond to hormones such as testosterone. When these hormones bind to receptors, they signal the muscle to repair and strengthen.
Consider them as doors that only open when the appropriate key (hormone) is used.
When the door opens, the body begins the process of protein synthesis and recovery.
More receptors can open up more pathways for growth signals.
Even high levels of testosterone would not cause muscle growth in the absence of these receptors.
Where Do Androgen Receptors Exist?
These receptors are spread throughout the body. They are found in various tissues, not just muscles.
- These receptors are present in the skeletal muscles, which include the arms, legs, chest, and back.
- They are also present in the brain, which is responsible for regulating energy and mood.
- It also plays a crucial role in enhancing the density and strength of bones.
- It also has beneficial effects on organs such as the liver and skin.
It demonstrates how hormones affect more than just muscles. They also have an impact on physical strength, mood, and recovery time.
How do they affect muscle growth?
Hormones activate the growth process when they bind to muscle receptors. This process involves:
- Protein synthesis is the process of producing new muscle tissue.
- This process also aims to reduce muscle breakdown.
- This process enhances strength by optimising the body’s energy utilisation.
This is why increased receptor activity frequently results in faster recovery and stronger muscles after training.
The concept of muscle saturation
Muscle saturation indicates that the receptors in the body are already filled or activated. Increasing hormones or stress does not result in more growth.
- Imagine you’re pouring water into a glass. When the glass is full, excess water spills out.
- Similarly, once receptors are fully employed, additional hormones may not produce better results.
- This is why some lifters do not experience continuous growth despite increasing their training or supplementation.
Can receptors become full?
Yes, receptors can become overloaded and unable to process additional signals. This is an example of muscle saturation.
- At first, new training or higher hormones may produce significant results.
- Over time, receptors may lose responsiveness.
- The body protects itself by preventing unlimited growth.
This explains why beginners grow quickly while advanced lifters frequently struggle for small gains.
Factors that affect receptor sensitivity
Not every receptor responds in the same way. Several factors can influence how well they function:
Genetics
Some individuals are born with more active receptors. They facilitate and expedite muscle growth.
Training style
- Heavy weight combined with proper rest improves receptor function.
- Overtraining may reduce their sensitivity.
Diet
- Enough protein and healthy fats promote receptor activity.
- Even if you train hard, a poor diet can slow your progress.
Rest and recover.
When you sleep, receptors help your muscles repair themselves. Poor sleep reduces their effectiveness.
Is it possible to increase androgen receptors?
Studies suggest that certain habits may improve receptor sensitivity:
- Strength training focuses on compound lifts such as squats and deadlifts.
- A proper diet includes enough protein, omega-3 fats, and micronutrients.
- Short breaks: Taking time off from training can refresh receptors.
- Avoiding stress: High stress hormones interfere with growth signals.
You can improve the effectiveness of existing receptors, but you cannot create an infinite number of them.
Misconceptions about saturation
Many lifters believe that taking more testosterone or supplements always results in more muscle. This is not correct.
- When receptors become saturated, excess hormones may be wasted.
- The body may even down-regulate receptors, reducing their sensitivity.
- Growth requires balance, not just pushing higher doses.
This is why smart training, diet, and recovery routines frequently produce better results than seeking shortcuts.
The Function of Natural Hormone Levels
Even without external assistance, the body produces enough testosterone for proper growth.
- Regular exercise naturally increases hormone release.
- Proper nutrition aids in maintaining strong levels.
- Stress management maintains hormone balance.
These natural signals are often sufficient for consistent progress, particularly for new lifters.
Practical Tips for Lifters:
To use receptors wisely and avoid saturation, take these steps:
- Train with a progressive overload mindset.
- Allow muscles enough time to rest.
- Eat a well-balanced diet that includes protein, carbohydrates, and fat.
- Sleep for at least 7–8 hours daily.
- Avoid prolonged periods of high stress.
These habits increase receptor activity and reduce the likelihood of hitting a growth plateau too soon.
Why do some lifters stop growing?
Growth may slow due to factors other than a lack of effort. It’s possible that receptors are saturated.
- The body adapts to training.
- The receptors become less responsive.
- More effort leads to lower returns.
At this point, changes Implementing a consistent routine, enhancing recovery, or adopting new training methods may be beneficial.